The production of printed circuit boards (PCBs) requires a wide range of materials and components. From the copper foil used in the board’s base layer, to various resistors, capacitors and integrated circuits – every component must be precisely manufactured for maximum performance.
In this article we will explore key materials and components that are essential for PCB production, as well as their importance within the industry.
Adhesives and Potting Compounds
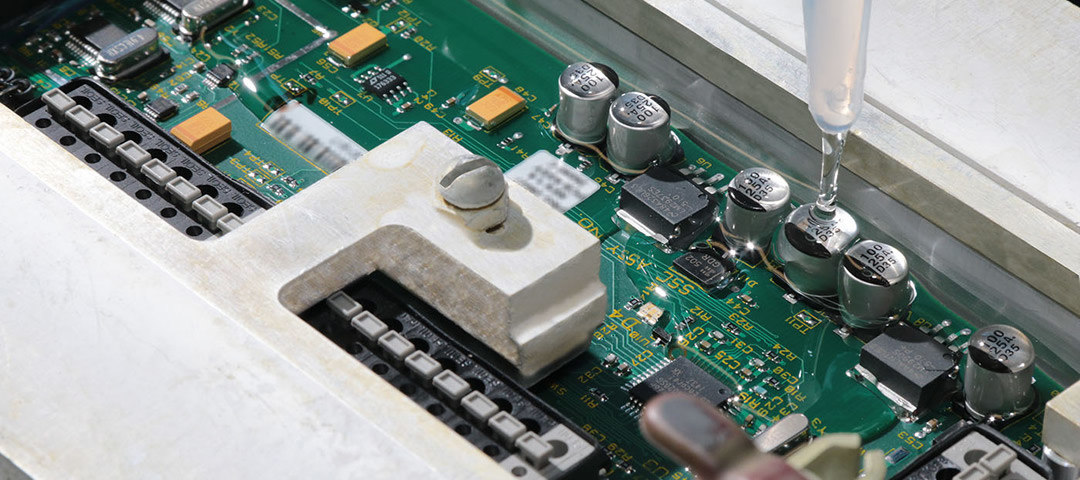

Adhesives and potting compounds are a crucial part of the assembly process for printed circuit boards (PCBs). These materials are used to hold components in place, create strong electrical connections between different parts, fill gaps, or protect the board from external elements.
Epoxy adhesives are one of the most common types used in PCB production. They have excellent adhesive properties and can resist heat, moisture and vibration for long-term reliability.
Acrylics and silicone-based adhesives are also popular options in PCB applications due to their superior flexibility when compared to epoxies. In addition to adhesives, potting compounds may be required depending on the application.
Potting compounds provide environmental protection by sealing out dust, dirt and moisture that could cause damage over time. Encapsulants such as urethanes or silicones can help protect sensitive components like integrated circuits from extreme temperatures or shock as well as serve as insulating media between conductors on the board itself.
Adhesive selection requires careful consideration based on factors such as temperature range requirements, electrical insulation needs, curing times and cost effectiveness—all important considerations when it comes to PCB production demands. Potting compounds should also be selected with these extremes in mind: after all they play an essential role in protecting against any potentially damaging conditions that a finished product might encounter during its lifetime
Circuit Board Traces
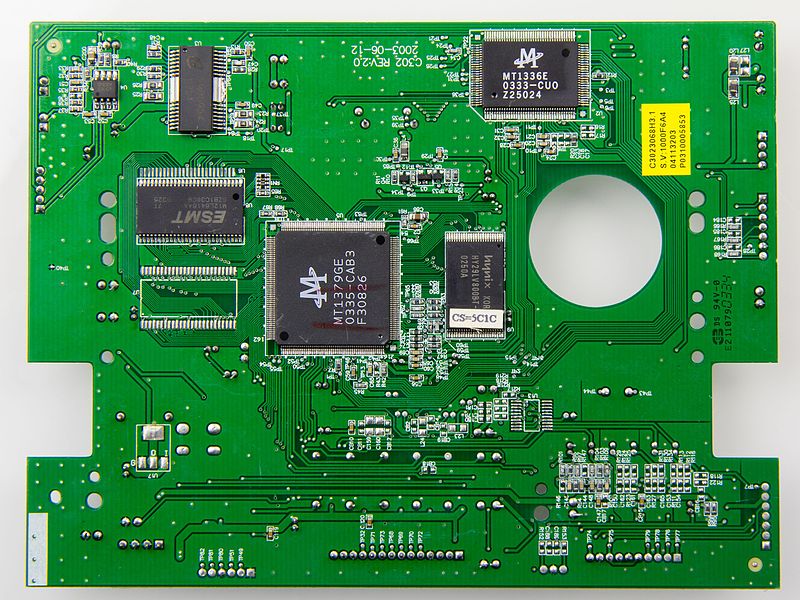
Circuit board traces are a key material and component used in PCB production. These traces, also known as copper paths, are created using etching techniques that involve applying an acid to the surface of the circuit board, which removes metal from specific areas.
This creates very thin lines or paths along the surface of the board that allow electricity to flow through it. Traces must be carefully designed and placed on a circuit board for optimal performance, making them essential components in any PCB production process.
The complexity of trace design can vary greatly depending upon its purpose; some may only require simple routes while others need multiple layers with more intricate designs for higher current carrying capacity and signal integrity purposes. In addition to being carefully planned out in terms of their layout on the circuit boards, traces must also be tested for accuracy by measuring their resistance or capacitance levels against established standards before they can be deemed suitable for use in any circuits.
Vias and Pads
Vias and pads are two of the most important components used in producing printed circuit boards (PCBs). Vias, or Dial connections, provide electrical pathways between different layers on a PCB.
They act as a conduit for signals from one layer to another, allowing data transmission and power flow throughout a board. Pads come in various sizes and shapes depending on their purpose; they can be used to mount components such as resistors or capacitors, connect multiple vials together, or provide an area for soldering wires to the board.
Together, vias and pads work hand-in-hand with other materials like copper foil and solder masking tape to create reliable electrical pathways within the PCB. While each component has its own unique function, it is essential that all of them work together correctly so that the desired outcome is reached: a fully functioning PCB.
Plated Through Holes (PTH) or Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Components
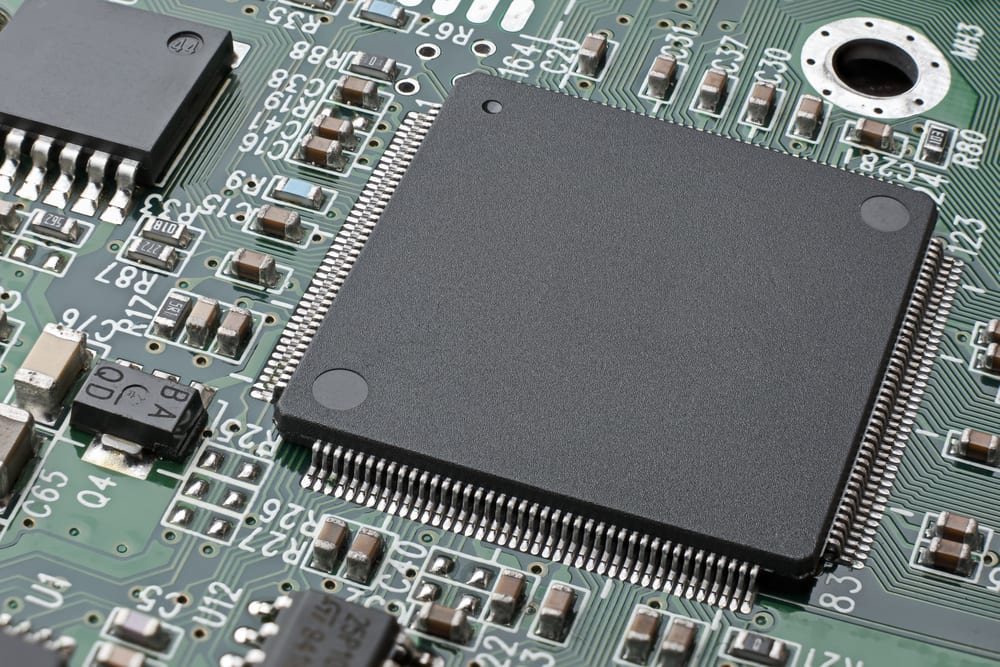

Plated Through Holes (PTH) and Surface Mount Technology (SMT) components are two key materials used in PCB production. PTH components use metal leads that pass through the board, while SMT components have flat contacts on their underside which sit directly on the surface of the board.
PTH components often provide greater electrical capacity as they require more space on a circuit board than SMT models, however they can be difficult to install due to their component size and shape. Conversely, SMT technology offers more flexibility in terms of design complexity and assembly requirements; these types of parts also tend to take up less space than PTH ones, making them well-suited for smaller designs with limited room for circuitry.
In addition to their differences in physical size and installation requirements, there is still much debate over which type of component performs better when it comes to overall functionality. Some people argue that PTH technology provides superior performance levels because its parts offer better heat dissipation compared with those from an SMT system due to their larger form factor; meanwhile others suggest that modern advances in electronics manufacturing technologies make this point moot as the performance gap between both types has been narrowed significantly by improved design techniques.
Ultimately though, selecting one type or another depends largely upon individual project needs – factors such as cost-efficiency and time constraints should all be taken into account before deciding whether or not either option is suitable for a given application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PCB Production relies heavily on the selection of key materials and components used in its production. These components are essential for ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications and performance levels.
With careful consideration given to these materials and components, manufacturers can produce high-quality printed circuit boards that meet all their requirements for both form and function.